Umn Ramp Calibration Strip Nitrogen is a methodological approach used by soil science labs to quantify nitrogen content through calibrated ramp strips. This guide explains how to plan, execute, and interpret results to ensure accurate, traceable measurements. By following practical steps, labs can reduce variability and improve data integrity.
Key Points
- Select appropriate N-concentration ramp standards aligned with the lab's typical soil N ranges.
- Standardize strip application to ensure reproducible surface area and contact with soil.
- Document lot numbers, expiration dates, and storage conditions for each strip.
- Use blank controls to detect background nitrogen signals and contamination.
- Regularly verify ramp linearity and re-calibrate with fresh materials every quarter.
What is Umn Ramp Calibration Strip Nitrogen?
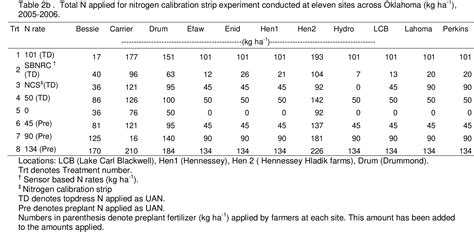
The Umn Ramp Calibration Strip Nitrogen concept centers on a calibrated strip that delivers a controlled nitrogen signal as part of a standard curve. Labs utilize this ramp to establish a predictable relationship between strip response and nitrogen concentration, enabling accurate translation of measured signals into meaningful soil N values. Emphasis is placed on traceability, documentation, and consistent handling to preserve data quality.
Applications in Soil Science Labs
In practice, this calibration method supports routine soil testing, research projects, and quality control programs. It helps laboratories compare results over time, across instruments, and between personnel. The approach is particularly valuable when measuring nitrogen in diverse soils, where matrix effects can otherwise obscure true nitrogen levels. Consistency across runs is achieved through standardized ramp materials and documented procedures.
Preparation and Standards
Preparation involves selecting ramp strips that cover the lab’s target nitrogen range, verifying their expiration dates, and storing them under recommended conditions. Standard operating procedures should outline strip handling, equilibration time, and any required blank or control measurements. Strong record-keeping ensures traceability from lot to data interpretation.
Calibration Procedures
Calibration procedures should define the exact steps for applying the ramp strip, timing, and reading the signal. Consistent environmental conditions (temperature, humidity) help minimize drift. Emphasize clean technique to prevent cross-contamination and ensure each strip is read using the same instrument settings.
Quality Control and Troubleshooting
Quality control includes routine checks of ramp linearity, control samples, and instrument performance. When irregularities arise—such as unexpected signal spikes or drifting readings—revisit strip storage, preparation steps, and instrument calibration. Document any deviations and corrective actions to maintain data transparency.
Interpreting Results and Data Integration
Interpreting results involves applying the calibration curve to convert strip responses into nitrogen concentrations, then integrating those values with soil metadata (pH, texture, moisture). Clear data visualization and reporting practices help stakeholders understand nitrogen status and support subsequent agronomic decisions. Always align interpretations with the calibration period and lot information of the strips used.
What is the main purpose of the Umn Ramp Calibration Strip Nitrogen in soil testing?
+The main purpose is to create a reliable, traceable reference that converts a strip signal into an accurate nitrogen concentration, helping labs maintain consistent measurements across runs, instruments, and operators.
How should ramp strips be stored to preserve accuracy?
+Store ramp strips in a cool, dry place away from direct light, with sealed packaging and documented lot numbers. Avoid exposure to moisture and high temperatures that can alter the strip's response.
What signs suggest calibration drift or strip degradation?
+Drift or degradation may be indicated by inconsistent readings across identical strips, changes in blank control responses, or a non-linear relationship in the calibration curve. Regular checks and comparing to recent control results help identify drift early.
Can Umn Ramp Calibration Strip Nitrogen be used with different soil types?
+Yes, but calibration should account for matrix effects. It’s advisable to select ramp strips that reflect the range of soil textures and organic matter in your lab’s typical samples, and to include matrix-matched controls when possible.
How often should calibration be validated in a busy lab?
+Calibration validation should be performed at least with each batch of strips and on a regular schedule (e.g., weekly or monthly) depending on throughput. Additional checks after instrument maintenance or environmental changes help ensure ongoing accuracy.
