Gmms In Machine Learning are a foundational probabilistic tool that models data as mixtures of Gaussian distributions, enabling nuanced representations of multimodal patterns. As the field advances, the future of Gmms In Machine Learning is being shaped by new algorithms, scalable training paradigms, and closer integration with deep learning workflows. This article surveys trends and innovations that are redefining how these models are built, deployed, and governed.
Key Points
- Scalable training of Gmms In Machine Learning using stochastic EM and variational techniques unlocks learning from large datasets without sacrificing interpretability.
- Hybrid models that combine GMMs with deep generative frameworks capture both multimodal distributions and rich dependencies in complex data.
- Online and continual learning capabilities enable GMM-based systems to adapt in real time to evolving environments and streams.
- Efficient inference in high-dimensional spaces is advancing through dimensionality reduction, factor analyzers, and product-of-Gaussians approximations.
- Probabilistic calibration and uncertainty quantification are becoming central to governance, risk assessment, and decision-making with Gmms In Machine Learning.
Understanding the Current Landscape of Gmms In Machine Learning
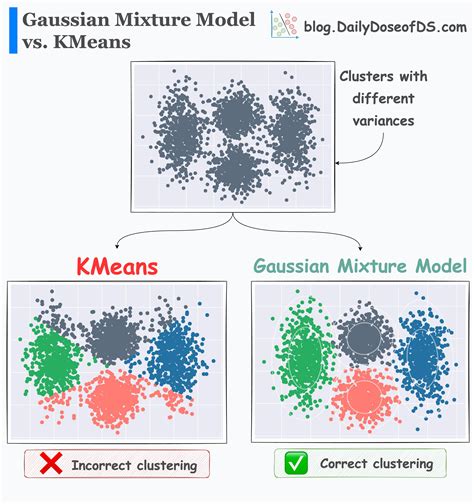
Today, Gmms In Machine Learning provide a flexible framework for clustering, density estimation, and anomaly detection. They offer interpretable probability-based insights that complement black-box models, making them valuable in domains where uncertainty matters. As practitioners combine GMMs with neural components, the line between traditional statistical modeling and modern deep learning continues to blur, yielding models that are both powerful and explainable.
Trends And Innovations On The Horizon
The next era for Gmms In Machine Learning is defined by integration, scalability, and smarter inference. The following trends illustrate where the field is headed.
Algorithmic Advances
New learning algorithms, including streaming EM variants and variational approximations, push GMMs toward real-time and large-scale applications. These methods preserve the probabilistic semantics of the model while improving convergence speed and robustness to noisy data.
Hybrid and Deep Integrations
Hybrid architectures blend Gaussian mixtures with neural networks to model both the latent structure and complex, high-dimensional features. Such hybrids enable richer representations for tasks like image and text analysis, where multimodality is the norm.
Data Efficiency and Transfer
Techniques that reuse learned components across tasks reduce data requirements and enable rapid adaptation. Transferable GMM components, shared latent spaces, and meta-learning-inspired updates are examples of this efficiency push.
Improvements In Inference, Interpretability, And Deployment
Advances in inference speed, interpretability, and deployment practices are making Gmms In Machine Learning more accessible in production settings. Probabilistic calibration helps teams quantify uncertainty, while structured priors and constraint-based learning improve model reliability in regulated industries.
Practical Implications For Businesses And Researchers
Organizations exploring probabilistic modeling benefit from the clarity Gmms In Machine Learning provide. The ability to quantify uncertainty, reason about multimodal data, and integrate with existing ML stacks makes GMM-based approaches compelling for anomaly detection, customer segmentation, and risk assessment. For researchers, these models offer fertile ground for theoretical exploration and cross-pollination with deep learning and probabilistic programming.
Ethics, Governance, And Responsible Use
As with any probabilistic model, responsible use of Gmms In Machine Learning involves transparency about assumptions, careful handling of sensitive data, and robust evaluation of potential biases. Implementations that include uncertainty estimates and audit trails are better suited for governance and compliance in high-stakes domains.
What exactly are Gmms In Machine Learning, and when should I consider using them?
+Gmms In Machine Learning refer to Gaussian Mixture Models applied to a wide range of learning tasks. They are particularly useful when your data exhibits multimodal distributions or when you need a probabilistic representation of uncertainty. Consider Gmms when you require interpretable clustering, density estimation, or a principled way to handle missing data and outliers, especially in domains where model transparency matters.
How do Gmms In Machine Learning compare to deep learning models for clustering and density estimation?
+Gmms offer explicit probabilistic foundations and interpretable components, which can be advantageous for understanding model behavior and uncertainty. Deep learning models can learn highly expressive representations but often require more data and can be harder to interpret. Hybrid approaches that combine GMMs with neural networks aim to blend the best of both worlds—robust probabilistic structure with rich feature representations.
What are the main challenges when deploying Gmms In Machine Learning at scale?
+Key challenges include achieving scalable parameter estimation on large datasets, maintaining numerical stability in high dimensions, integrating with existing ML pipelines, and ensuring timely inference for real-time applications. Addressing these requires scalable EM or variational methods, efficient data handling, and careful engineering of deployment environments to preserve probabilistic guarantees.
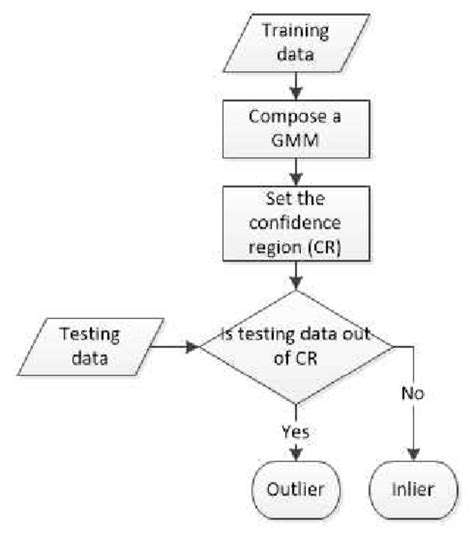
How can I evaluate the quality and reliability of a GMM in practice?
+Assessment combines statistical criteria (like BIC/AIC, cross-validated likelihood) with practical measures (calibration of probability estimates, clustering stability, and downstream task performance). Visual diagnostics for component overlap and posterior responsibilities, along with uncertainty quantification, help validate reliability in real-world settings.
What role do Gmms In Machine Learning play in anomaly detection and clustering?
+GMMs naturally support anomaly detection by assigning low-probability regions to data points, highlighting unusual patterns. In clustering, they provide probabilistic assignments and soft clustering that captures uncertainty about group membership. This makes them effective in domains where data exhibits clear multimodality but also contains outliers or novel patterns.