39 Degrees Fahrenheit To Celsius: Understanding the Benchmark in Cold Chains
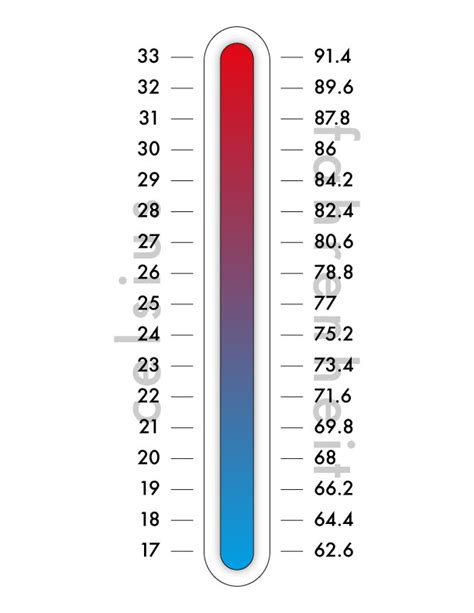
Converting 39 Degrees Fahrenheit To Celsius translates to about 3.9°C, a commonly cited reference point for refrigerated storage and transport. This article explores how that conversion affects costs across the cold chain—from energy consumption and equipment sizing to spoilage risk and regulatory compliance—and offers practical steps to optimize performance without compromising product quality.
What 39 Degrees Fahrenheit To Celsius Means for Temperature Control
In many industries, 39 Degrees Fahrenheit To Celsius is used as a practical guideline for perishable items such as dairy, meat, and certain pharmaceuticals. Maintaining this target, and understanding the margin around it, helps prevent energy waste, reduces the likelihood of temperature excursions, and supports consistent product quality. Even small deviations can translate into tangible cost impacts, particularly when scaled across warehouses, fleets, and seasonal demand.
Cost Drivers Linked to the 3.9°C Benchmark
Key cost drivers include energy use, equipment efficiency, insulation performance, labor to manage excursions, and spoilage risk. Because 3.9°C sits close to the threshold where microbial growth accelerates for many products, facilities focus on tight control, data visibility, and proactive maintenance to avoid costly waste or recalls. Regulatory compliance, such as traceability and temperature logs, also adds cost when standards are strict.
Key Points
- Operational energy costs are highly sensitive to small shifts around 3.9°C, so precise control minimizes wasted cooling.
- Hot or cold spots within pallets can lead to product damage and recalls, increasing spoilage-related costs.
- Choosing the right refrigeration equipment and insulation at this temperature range reduces maintenance and energy use.
- Real-time monitoring and alerting help avoid expensive temperature excursions and compliance penalties.
- Logistics planning (loading, transit, and handoffs) around 39 Degrees Fahrenheit To Celsius can optimize route efficiency and reduce handling costs.
Strategies to Optimize Costs While Keeping Cold Chains Intact
Adopting precise temperature control, improving insulation, and deploying smart sensors can yield meaningful savings around the 3.9°C target. Practical steps include calibrating thermostats, using data loggers that flag excursions in real time, optimizing pallet layout to reduce heat transfer, and scheduling transport to minimize dwell times in non-ideal conditions. By aligning equipment capability with the 39 Degrees Fahrenheit To Celsius target, organizations can lower energy use, extend shelf-life where appropriate, and reduce waste.
What is the exact Celsius equivalent of 39 Degrees Fahrenheit To Celsius?
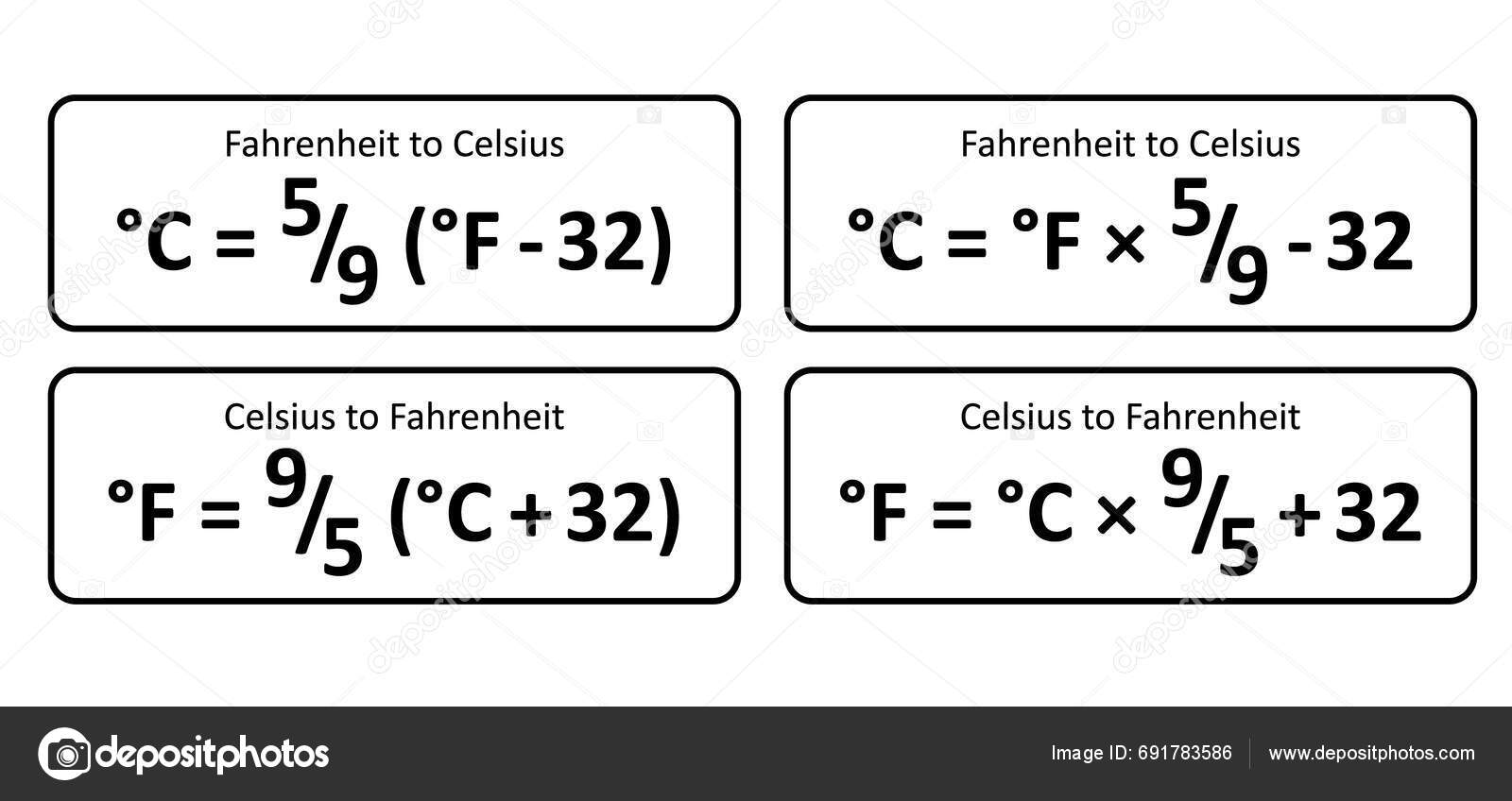
+The Celsius equivalent of 39 Degrees Fahrenheit To Celsius is approximately 3.9°C (calculated using C = (F − 32) × 5/9). This falls just under 4°C and is a common reference point in cold-chain planning.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Why does this specific temperature matter for cost in cold chains?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>This temperature is near the threshold where many perishable goods shift from stable to marginally risky in terms of microbial growth and chemical changes. Staying close to 3.9°C minimizes energy use while reducing spoilage risk, thus impacting total cost of ownership.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What are effective ways to manage costs around this temperature?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Invest in precise temperature control, calibrated sensors, regular maintenance, and data analytics to detect excursions early. Combine with insulation improvements, optimized routing, and smart scheduling to minimize energy use and waste.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How can I calculate the Celsius value quickly for planning?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Use the formula C = (F − 32) × 5/9. For 39°F, C ≈ (39 − 32) × 5/9 = 7 × 5/9 ≈ 3.9°C. This quick check helps in fast planning and decision-making.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Are there regulatory considerations tied to this temperature?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Yes. Many cold-chain standards require consistent recording of temperatures, alerting on excursions, and clear documentation for audits. Aligning operations to the 3.9°C target helps maintain compliance while controlling costs.</p>
</div>
</div>